How to Calculate Interest Receivable and Interest Revenue for Notes Receivable The Motley Fool
A company recognizes revenue under that principle by applying a 5-step model as follows. Top 10 differences between IFRS 15 and ASC Topic 606 for revenue recognition. A leveraged buyout (LBO) is a transaction in which a company or business is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition.
Net interest income
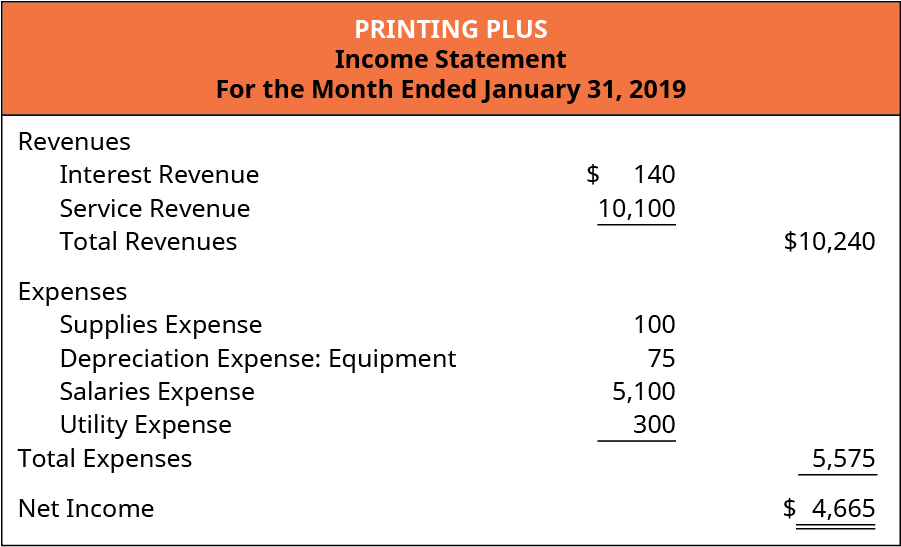
A note falling due on a Sunday or a holiday is due on the next business day. Interest Revenue improves a company’s profitability, provides a reliable source of cash inflow, and can help assess the efficiency of investments and inform future financial decisions. Delve into the realm of Business Studies with a comprehensive guide on Interest Revenue. This pivotal topic is discussed in detail, from uncovering the definition of interest revenue to understanding its role as an asset or liability.
Standards and frameworks
IAS 18 states that ‘Revenue shall be measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable’ (12). In determining fair value it would be necessary to take into account any trade discounts or volume rebates granted will i be a taskrabbit employee by the seller. As long as the interest is not received, it is included in the interest receivable account, any changes in the balance marked by the receipt or issuance of interest revenue, will reflect in this account.
Products
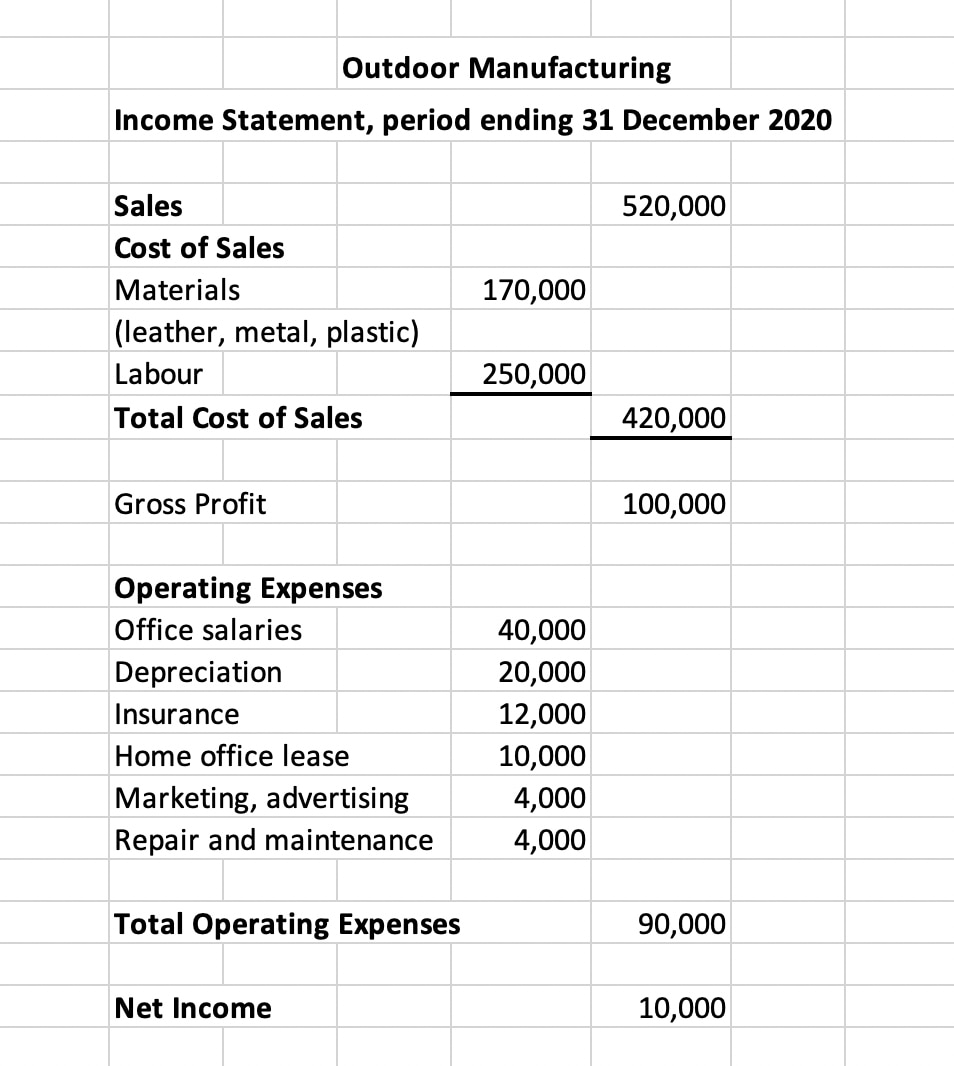
In such cases, the interest income is generated for these companies from ancillary activities. These companies record interest income in the ‘Other Revenue and Expense’ section of the income statement. The recording of interest revenue in the income statement depends on the nature of the business.
Interest income is revenue for the payee and an expense for the payer. Interest revenue increases the payee’s tax liability and reduces the payee’s tax liability because interest expense is tax deductible. Using this formula, we can calculate interest revenue in the previous example.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Capital Account Activity in Pass-through Entities
The company can make the interest income journal entry by debiting the interest receivable account and crediting the interest income account. In this case, your company will need to account for accrued interest revenue on Dec. 31, 2015, to close out the books for the month and year, well before the note comes due on Feb. 8, 2016. This happens frequently in accrual accounting — revenue is recognized before it is received in cash. Sales of nonfinancial assets, such as property, plant and equipment (IAS 16), intangible assets (IAS 38) and investment property (IAS 40), are accounted for using the measurement and derecognition guidance of IFRS 15. A bank’s main goal is to increase the net interest income it receives.
- The US GAAP policy election simplifies the accounting for sales taxes compared to IFRS Standards, but may yield a different presentation and transaction price when elected.
- Other annual disclosures about revenue are typically not required for interim financial reporting.
- Frequency of a year is the amount of time for the note and can be either days or months.
The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. It’s also worth noting that this revenue stream has a significant impact on the company’s financial statements. It affects the income statement where it increases total revenue and net income, and it also impacts the balance sheet, contributing to the increase in total assets. Interest revenue is the income earned from the lending of assets, whether it be money, goods or services. The US GAAP policy election simplifies the accounting for sales taxes compared to IFRS Standards, but may yield a different presentation and transaction price when elected. For example, if a company has received $10,000 in interest payments during a particular quarter and accrued another $5,000 in owed interest, then it would report $15,000 in interest revenue under the accrual method.
This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors. Learn to calculate accrued interest on loans or credit cards, considering rates, daily balances, and precision methods. To calculate interest revenue for the 21 days up to the end of the year, you would follow the same steps as in the interest receivable example. Suppose a company issues a $10,000 note at 9% annual interest to your company that will mature in 60 days.
